Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
Potential of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source in gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the screening of urinary exogenous androgenic anabolic steroids
| dc.contributor.author | Raro Macián, Montserrat | |
| dc.contributor.author | Portoles, Tania | |
| dc.contributor.author | Pitarch, Elena | |
| dc.contributor.author | Sancho, Juan V | |
| dc.contributor.author | Hernandez, Felix | |
| dc.contributor.author | Garrostas, L. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Marcos, Josep | |
| dc.contributor.author | Ventura, Rosa | |
| dc.contributor.author | Segura, Jordi | |
| dc.contributor.author | Pozo, Óscar J. | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2016-01-25T10:37:19Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2016-01-25T10:37:19Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2016-02-04 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | RARO, M., et al. Potential of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source in gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the screening of urinary exogenous androgenic anabolic steroids. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, vol. 906, p. 128-138. | ca_CA |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0003-2670 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10234/146529 | |
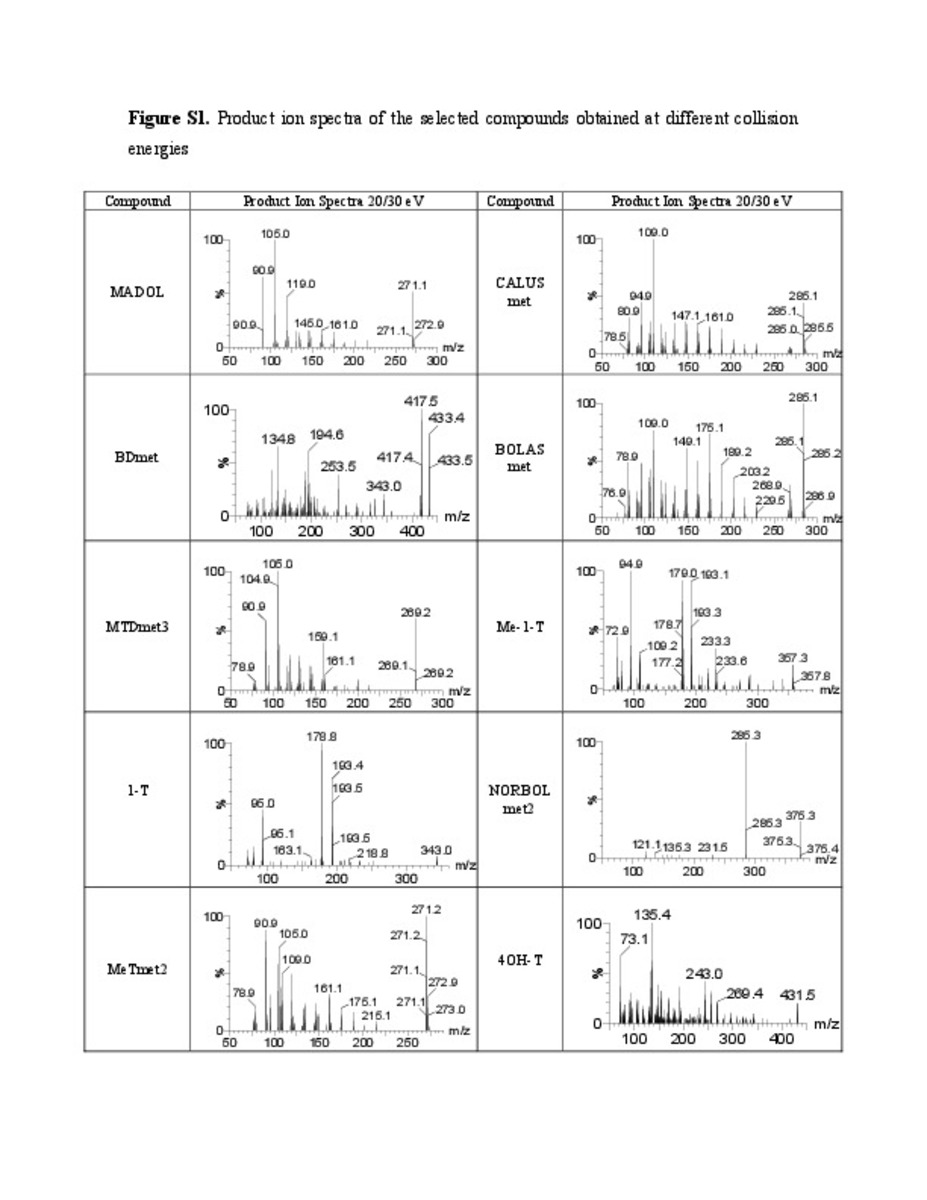
| dc.description.abstract | The atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) source for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis has been evaluated for the screening of 16 exogenous androgenic anabolic steroids (AAS) in urine. The sample treatment is based on the strategy currently applied in doping control laboratories i.e. enzymatic hydrolysis, liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) and derivatization to form the trimethylsilyl ether-trimethylsilyl enol ether (TMS) derivatives. These TMS derivatives are then analyzed by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry using a triple quadrupole instrument (GC-QqQ MS/MS) under selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mode. The APCI promotes soft ionization with very little fragmentation resulting, in most cases, in abundant [M + H]+ or [M + H-2TMSOH]+ ions, which can be chosen as precursor ions for the SRM transitions, improving in this way the selectivity and sensitivity of the method. Specificity of the transitions is also of great relevance, as the presence of endogenous compounds can affect the measurements when using the most abundant ions. The method has been qualitatively validated by spiking six different urine samples at two concentration levels each. Precision was generally satisfactory with RSD values below 25 and 15% at the low and high concentration level, respectively. Most the limits of detection (LOD) were below 0.5 ng mL−1. Validation results were compared with the commonly used method based on the electron ionization (EI) source. EI analysis was found to be slightly more repeatable whereas lower LODs were found for APCI. In addition, the applicability of the developed method has been tested in samples collected after the administration of 4-chloromethandienone. The highest sensitivity of the APCI method for this compound, allowed to increase the period in which its administration can be detected. | ca_CA |
| dc.description.sponsorShip | Ministry of Education and Science, Spain, in the project DEP2011-28573-C02-01/02 Generalitat Valenciana (Research Group of Excellence Prometeo II/2014/023; ISIC EnviFood 2012/016) | |
| dc.format.extent | 11 p. | ca_CA |
| dc.format.mimetype | application/pdf | ca_CA |
| dc.language.iso | eng | ca_CA |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | ca_CA |
| dc.relation.isPartOf | Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, vol. 906 | ca_CA |
| dc.rights | Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. | ca_CA |
| dc.rights.uri | http://rightsstatements.org/vocab/InC/1.0/ | * |
| dc.subject | Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) | ca_CA |
| dc.subject | Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) | ca_CA |
| dc.subject | Gas chromatography (GC) | ca_CA |
| dc.subject | Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) | ca_CA |
| dc.subject | Triple quadrupole (QqQ) | ca_CA |
| dc.subject | Doping control analysis | ca_CA |
| dc.title | Potential of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source in gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the screening of urinary exogenous androgenic anabolic steroids | ca_CA |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | ca_CA |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.041 | |
| dc.rights.accessRights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | ca_CA |
| dc.relation.publisherVersion | http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003267015300337 | ca_CA |
| dc.edition | Postprint | ca_CA |
| dc.type.version | info:eu-repo/semantics/submittedVersion |
Ficheros en el ítem
Este ítem aparece en la(s) siguiente(s) colección(ones)
-
IUPA_Articles [307]